Esports Players Play Better Online
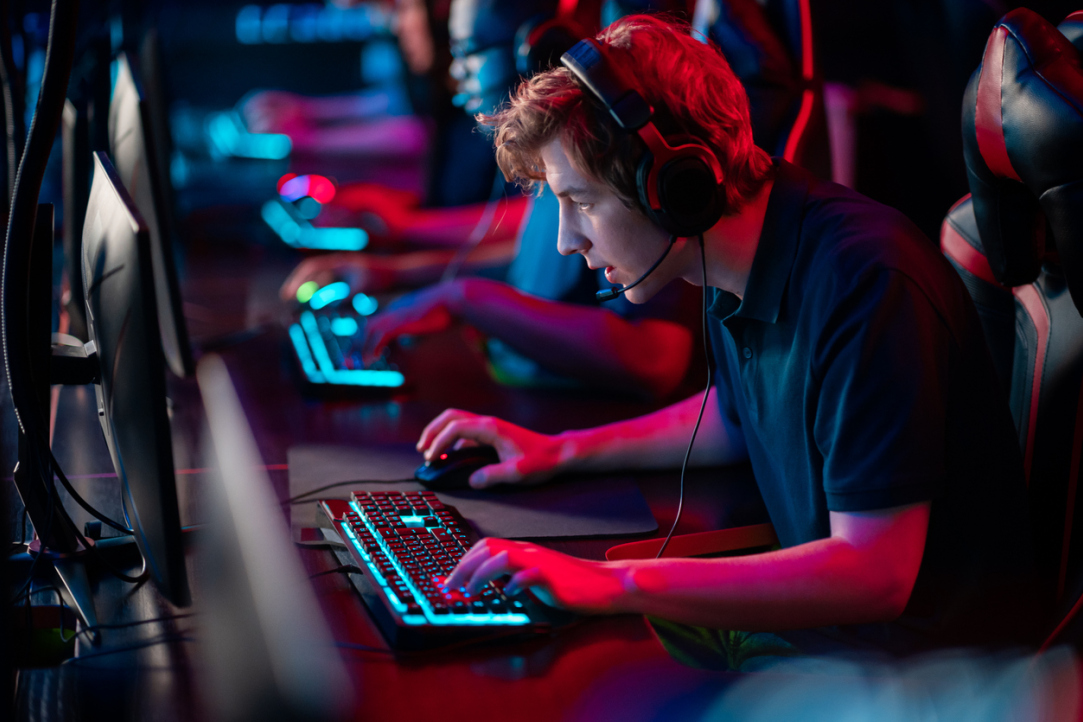

In competitions, esports players, like other athletes, face stress and show worse results due to pressure. A substantial decrease takes place in the performance of esports players during overtime. This effect, however, is significantly mitigated in online competitions compared to live events—the difference can reach 30%. A study by a team of authors from HSE University’s Moscow and Perm campuses and European University Viadrina (Germany) explores the phenomenon of choking under pressure within the context of esports. The study was published in the Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization.
Esports is a multibillion-dollar industry with major tournaments and million-dollar prizes. In addition, in Russia, esports has become a priority area of development. As in traditional sports, both technical skills and psychological stability are key to success. Understanding how stress affects the performance of players will help to improve the training process and achieve better results.

Gleb Vasiliev
Gleb Vasiliev, Junior Research Fellow at the Laboratory of Sports Studies of the Faculty of Economic Sciences, Petr Parshakov and Iuliia Naidenova, staff members of the International Laboratory of Intangible-driven Economy at HSE University in Perm, and Igor Tylkin, researcher at European University Viadrina, studied the behaviour of esports players in the game Counter-Strike: Global Offensive (CS:GO).

Petr Parshakov
CS:GO is a competitive online shooter in which two teams of five players compete. Matches are usually played on 1–5 maps, which in turn consist of short rounds. To win the round, teams must either complete a specific task or eliminate their opponents. Usually, 30 rounds are played on one map in competitions. When a team wins at least 16 of them, it wins the map. In the event of a draw, additional rounds are played: at 15:15, overtime starts. The team of scientists analysed players’ behaviour in overtime.

Iuliia Naidenova
The authors studied statistics from almost a million games for the period from 2012 to 2022 among players with both high and low ratings. The sample included more than 1,700 esports players. The researchers used two key indicators.
The first was individual performance, which included the player’s rating (calculated by comparing a player's average performance statistics to the same averages for CS:GO in general calculated over a period of time) and the percentage of accurate shots. These metrics reflect the level of skill in difficult conditions. The second is team coordination, ie cases of ‘friendly fire’ (causing damage to teammates). An increase in the number of hits on teammates may indicate tension and problems with communication in the team. Pressure and stress were measured by analysing overtimes—additional rounds that are played to determine the winner in the event of an equal outcome in matches. As in traditional sports, in extra time, the result of the game most often depends on numerous small factors. In addition, the authors studied the impact of the game format: whether it was an on-site performance or an online tournament. Approximately 70% of the matches were played online, and overtimes were played in 9% of them.
It turned out that overtimes do cause players significant stress. On average, they lead to a decrease in player ratings by almost 2%, and the percentage of accurate shots decreased by 7%. This decline was evident in both professional and novice players. ‘The results of our study show that although experienced players outperform their less experienced counterparts in all game formats, this advantage may fade away in overtime,’ noted the authors. The probability of errors leading to friendly fire also increased.
The tournament format plays an important role. When competitions are held online, with no audience or unnecessary excitement, players perform about 30% better than during on-site matches. Researchers attribute this to a psychological factor—the presence of fans increases stress.
The researchers note that the results of the study can be applied in various fields. For example, it is worth considering that the format of work (on-site or online) significantly influences stress levels and their impact on team coordination and individual results. ‘Esports is a good platform for testing such effects. Players’ high cognitive activity and team coordination are essential in the game, which makes it a convenient object for analysing behaviour under pressure. The study results can be useful for HR departments and crisis management, as well as in fields where teamwork and productivity under pressure are important, such as IT consulting or startups,’ the authors added.
See also:
Scientists Test Asymmetry Between Matter and Antimatter
An international team, including scientists from HSE University, has collected and analysed data from dozens of experiments on charm mixing—the process in which an unstable charm meson oscillates between its particle and antiparticle states. These oscillations were observed only four times per thousand decays, fully consistent with the predictions of the Standard Model. This indicates that no signs of new physics have yet been detected in these processes, and if unknown particles do exist, they are likely too heavy to be observed with current equipment. The paper has been published in Physical Review D.
HSE Scientists Reveal What Drives Public Trust in Science
Researchers at HSE ISSEK have analysed the level of trust in scientific knowledge in Russian society and the factors shaping attitudes and perceptions. It was found that trust in science depends more on everyday experience, social expectations, and the perceived promises of science than on objective knowledge. The article has been published in Universe of Russia.
Scientists Uncover Why Consumers Are Reluctant to Pay for Sugar-Free Products
Researchers at the HSE Institute for Cognitive Neuroscience have investigated how 'sugar-free' labelling affects consumers’ willingness to pay for such products. It was found that the label has little impact on the products’ appeal due to a trade-off between sweetness and healthiness: on the one hand, the label can deter consumers by implying an inferior taste, while on the other, it signals potential health benefits. The study findings have been published in Frontiers in Nutrition.
HSE Psycholinguists Launch Digital Tool to Spot Dyslexia in Children
Specialists from HSE University's Centre for Language and Brain have introduced LexiMetr, a new digital tool for diagnosing dyslexia in primary school students. This is the first standardised application in Russia that enables fast and reliable assessment of children’s reading skills to identify dyslexia or the risk of developing it. The application is available on the RuStore platform and runs on Android tablets.
Physicists Propose New Mechanism to Enhance Superconductivity with 'Quantum Glue'
A team of researchers, including scientists from HSE MIEM, has demonstrated that defects in a material can enhance, rather than hinder, superconductivity. This occurs through interaction between defective and cleaner regions, which creates a 'quantum glue'—a uniform component that binds distinct superconducting regions into a single network. Calculations confirm that this mechanism could aid in developing superconductors that operate at higher temperatures. The study has been published in Communications Physics.
Neural Network Trained to Predict Crises in Russian Stock Market
Economists from HSE University have developed a neural network model that can predict the onset of a short-term stock market crisis with over 83% accuracy, one day in advance. The model performs well even on complex, imbalanced data and incorporates not only economic indicators but also investor sentiment. The paper by Tamara Teplova, Maksim Fayzulin, and Aleksei Kurkin from the Centre for Financial Research and Data Analytics at the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences has been published in Socio-Economic Planning Sciences.
Larger Groups of Students Use AI More Effectively in Learning
Researchers at the Institute of Education and the Faculty of Economic Sciences at HSE University have studied what factors determine the success of student group projects when they are completed with the help of artificial intelligence (AI). Their findings suggest that, in addition to the knowledge level of the team members, the size of the group also plays a significant role—the larger it is, the more efficient the process becomes. The study was published in Innovations in Education and Teaching International.
New Models for Studying Diseases: From Petri Dishes to Organs-on-a-Chip
Biologists from HSE University, in collaboration with researchers from the Kulakov National Medical Research Centre for Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Perinatology, have used advanced microfluidic technologies to study preeclampsia—one of the most dangerous pregnancy complications, posing serious risks to the life and health of both mother and child. In a paper published in BioChip Journal, the researchers review modern cellular models—including advanced placenta-on-a-chip technologies—that offer deeper insights into the mechanisms of the disorder and support the development of effective treatments.
Using Two Cryptocurrencies Enhances Volatility Forecasting
Researchers from the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences have found that Bitcoin price volatility can be effectively predicted using Ethereum, the second-most popular cryptocurrency. Incorporating Ethereum into a predictive model reduces the forecast error to 23%, outperforming neural networks and other complex algorithms. The article has been published in Applied Econometrics.
Administrative Staff Are Crucial to University Efficiency—But Only in Teaching-Oriented Institutions
An international team of researchers, including scholars from HSE University, has analysed how the number of non-academic staff affects a university’s performance. The study found that the outcome depends on the institution’s profile: in research universities, the share of administrative and support staff has no effect on efficiency, whereas in teaching-oriented universities, there is a positive correlation. The findings have been published in Applied Economics.